
Stroke Quality & Outcomes
After having been a certified Advanced Primary Stroke Center since 2011, Redlands Community Hospital was certified by The Joint Commission as an Advanced Thrombectomy Capable Stroke Center in 2020.
RCH expanded its neuroscience program services to include advanced and complex neurosurgical and neuroendovascular therapies for both Ischemic (blocked) and Hemorrhagic (bleed) types of stroke and other neurological disease conditions.
The completion of the 1100 square foot Hybrid Neurointerventional/ Neurosurgical Operating Room Suite, the first of its kind in the Inland Empire, the ongoing ESRI Emergency Room expansion and remodeling with a dedicated Stroke Treatment Room and CT scanner, and the latest certification by The Joint Commission, is a testament to the organization’s commitment to providing quality care in the region.
Redlands Community Hospital offers diagnostic cerebral angiography and other neuroendovascular/ neurosurgical treatment procedures (glossary below) such as:
- Endovascular coiling and surgical clipping for brain aneurysms
- Wada testing
- Carotid stenting
- Intracranial angioplasty and embolization
- Carotid endarterectomy
- Lumbar drain placement
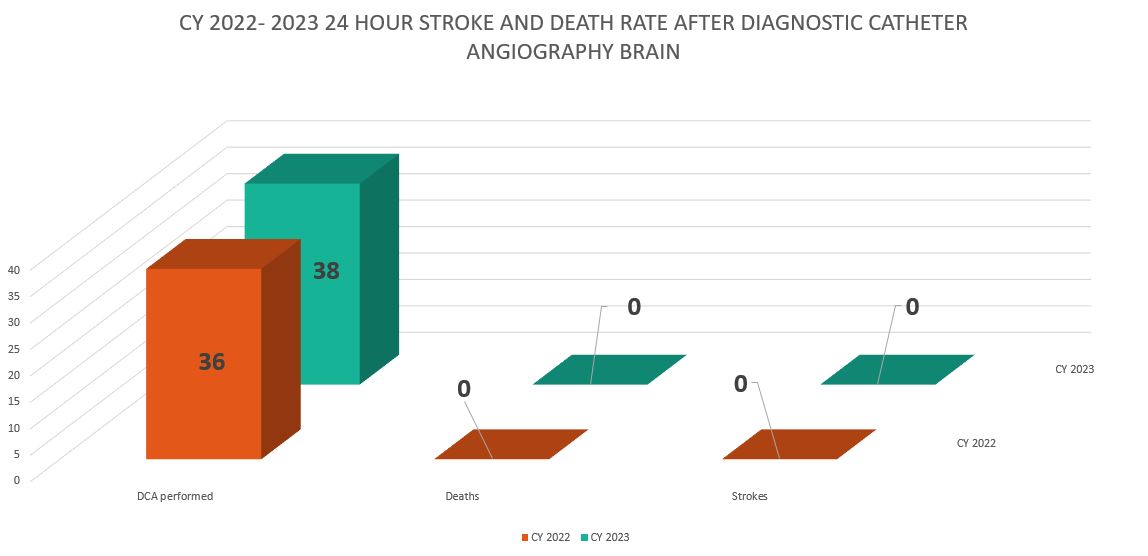
In 2023 Redlands Community Hospital performed 38 diagnostic catheter angiography of brain. No cases resulted in stroke or death within 24 hours of the procedure.
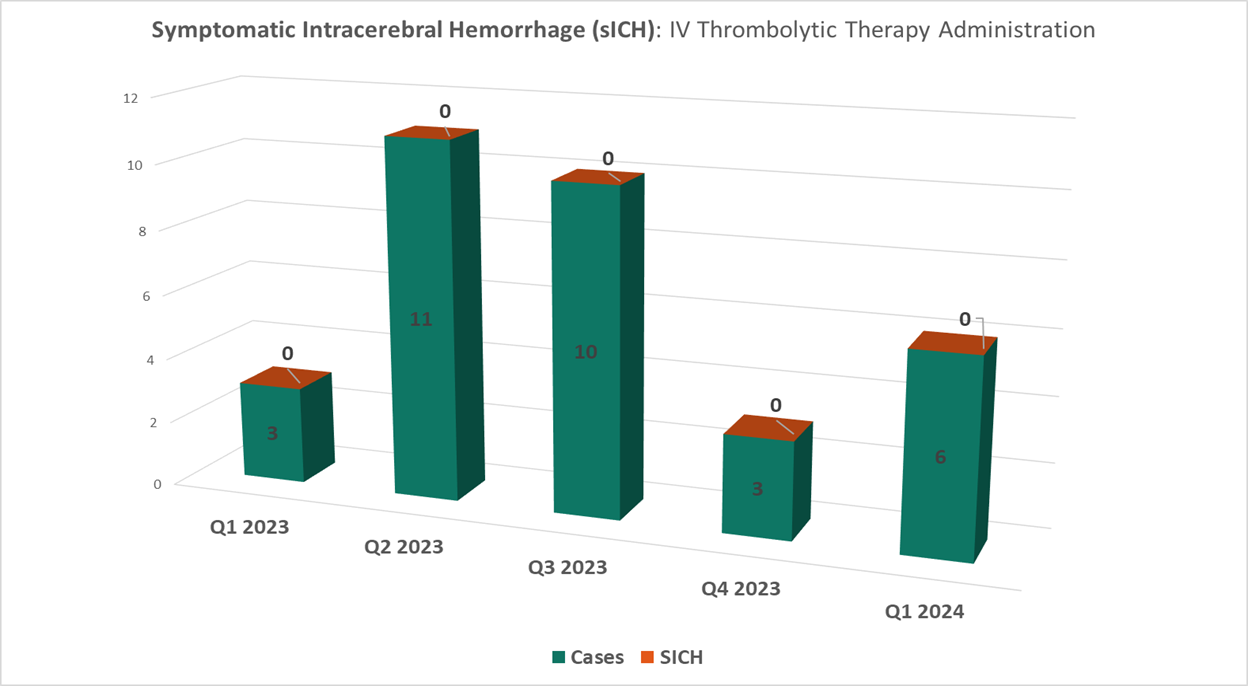
Symptomatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) with Intravenous Thrombolytic Therapy
In 2023 and 1st quarter of 2024, RCH has had no cases where a hemorrhagic transformation occurred in cases where intravenous thrombolytics were administered to eligible ischemic stroke patients.
Percentage of Acute Ischemic Strokes Treated with IV Thrombolytic and Discharged Home
In 2023, almost fifty percent (48%) of ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolytic were discharged to their homes directly. This meant they did not have to go to rehabilitation facilities after their hospital stay.

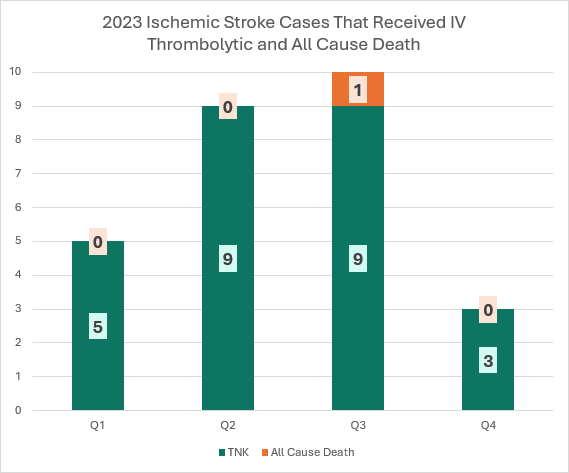
Mortality in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients that Received Thrombolytic Therapy
In 2023, one death occurred out of 27 ischemic stroke patients receiving intravenous thrombolytic treatment.
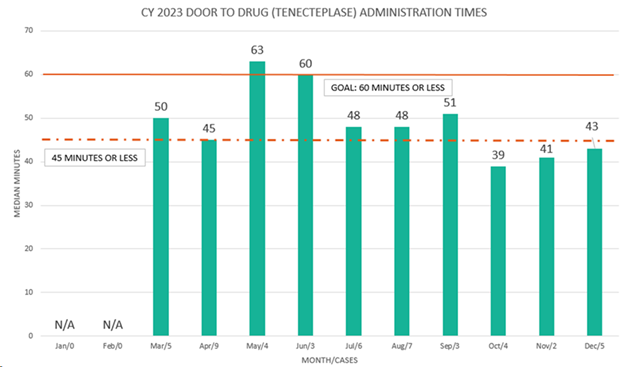
In 2023, Redlands Community Hospital surpassed the 60-minute goal for door-to-drug therapy in the treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke patients and is working on sustaining achievement of the 45-minute or less goal for the same patient population.
With state-of-the-art equipment and neuroendovascular physician expertise, the RCH stroke program now provides 24/7 treatment for eligible stroke patients for mechanical endovascular reperfusion therapy or thrombectomy, which is a procedure to remove blood clots causing blockage to critical parts of the brain, and restore blood flow to allow the highest chance of recovery for the patient. The RCH team works hard to improve blood flow to blocked areas of the brain as much as possible, and achieving that technical goal is even more rewarding when the stroke patient starts manifesting the resolution of their deficits.
Recognition and Achievement
Since 2014, Redlands Community Hospital’s Stroke Program has been recognized by the American Heart Association/ American Stroke Association’s Get With The Guidelines-Stroke for quality achievement in stroke care and timeliness in providing stroke treatment to eligible patients.

- 2023 Gold Plus Target: Stroke Honor Roll Elite
- 2022 Gold Plus Target: Stroke Honor Roll Elite, Type 2 Diabetes Honor Roll
- 2021 Gold Plus Target: Stroke Honor Roll, Target: Type 2 Diabetes Honor Roll
- 2020 Gold Plus Target: Type 2 Diabetes Honor Roll
- 2019 Gold Plus Target: Stroke Honor Roll Elite

For more information on our Stroke Program and services, please call (909)335-5501 or email StrokeProgram@redlandshospital.org
Definitions
Carotid endarterectomy: a surgical procedure used to reduce the risk of stroke by correcting stenosis (narrowing) of the common artery or internal carotid artery.
Carotid stenting: a procedure that opens clogged arteries to restore blood flow to the brain. They are often performed to treat or prevent stroke.
Cerebral angiography: a diagnostic technique that uses an X-ray imaging guidance and a special dye, known as contrast, to determine the health of blood vessels in the brain and evaluate blow flow.
Endovascular coiling: a procedure performed to block blood flow into an aneurysm (a weakened area in the wall of an artery).
Mechanical endovascular reperfusion therapy or thrombectomy: emergent treatment for stroke that removes larger clots that block large blood vessels in the brain.
Intracranial angioplasty and embolization: used to widen blood vessels in the brain and treat abnormal blood vessels in the brain.
Lumbar drain placement: a procedure to place a small tube in your lower back and into the spinal column to drain or collect cerebral spinal fluid.
Wada testing: Named after a Japanese physician who first performed it, this is a test used to inform doctors about which side of the brain controls language and the importance of the side of the brain concerning memory function.